
This way, you can see how much profit or loss your business generates during a reporting period. Non-operating revenue is typically found below operating income and above net income/profit in your financial statement. The primary way of generating revenue is through selling your product or delivering a service. You can clearly see your business’s profitability over a given reporting period. The parts of the income statement before taxes and interest show your company’s EBIT, or earnings before interest and taxes. Unlike net profit (the bottom line of the P&L), gross profit shows you your company’s profit before subtracting expenses.
COGS (Cost of Goods Sold, aka Cost of Sales)
Revenue, including non-operating income, is $842,000 ($834,000 net sales + $5,000 interest income + $3,000 other income). The balance sheet is a powerful analytical tool for investors and creditors, but it doesn’t provide a full understanding of your company’s value. Assets are anything your business owns, including cash, accounts receivable, inventory, machinery, and property. Intangible assets, things of value that you can’t touch or feel, are included here, too.
Top Picks for Ecommerce Accounting Software
For instance, a consulting company may earn some rental revenue from properties owned. This will be non-operating revenue, not tied to the core consulting business. In addition, interest income earned from capital lying in the bank is also part of a non-operating revenue portfolio. While both of these metrics denote profits made, Gains refer to profits that don’t relate to the core business of the company. They are mostly made from one-time non-business activities that might not re-occur in the future. For instance, these could be assets accrued from the sale of land or an old vehicle.
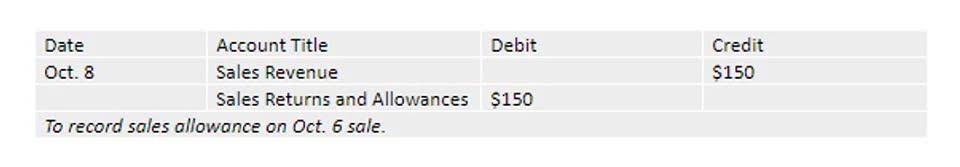
Summary Comparison of the Three Financial Statements
HBS Online does not use race, gender, ethnicity, or any protected class as criteria for admissions for any HBS Online program. Our easy online application is free, and no special documentation is required. All participants must be at least 18 years of age, proficient in English, and committed to learning and engaging with fellow participants throughout the program. HBS Online does not use race, gender, ethnicity, or any protected class as criteria for enrollment for any HBS Online program. Our easy online enrollment form is free, and no special documentation is required.

Gross profit tells you your business’s profitability after considering direct costs but before accounting for overhead costs. There is no gross profit subtotal, as the cost of sales is grouped with all other expenses, which include fulfillment, marketing, technology, content, general and administration (G&A), and other expenses. The statement is divided into time periods that logically follow the company’s operations. The most common periodic division is monthly (for internal reporting), although certain companies may use a thirteen-period cycle. These periodic statements are aggregated into total values for quarterly and annual results. Financial analysis of an income statement can reveal that the costs of goods sold are falling, or that sales have been improving, while return on equity is rising.

Gains represent all other sources of income apart from the company’s main business activities. This represents the profit that a company has earned for the period, after https://www.bookstime.com/ taking into account all expenses. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) permits businesses to deduct operating expenses if the business operates to gain profits.
What financial insights can be gleaned from comparing consecutive income statements?
For a company offering subscription or consulting services, operating revenue will be the fees earned for services rendered. It shows you how much money flowed into and out of your business over a certain period of time. A balance sheet shows you how much you have (assets), how much you owe (liabilities), and how much is remains (equity). It’s a snapshot of your whole business as it stands income statement accounts at a specific point in time. These expenses are listed individually here, but some income statements will bundle these and other similar expenses together into one broad category called “Selling, General & Administrative Expenses” (SG&A). When a business owner makes an income statement for internal use only, they’ll sometimes refer to it as a “profit and loss statement” (or P&L).
- Because of this, horizontal analysis is important to investors and analysts.
- This is because lenders want to know the ability of the company to generate revenue and profit, as well as its capacity to repay the loan.
- The income statement shows the financial health of a company and whether or not a company is profitable.
- While an income statement displays a company’s financial performance over a specific period (e.g. a quarter or a year), a balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a given moment in time.
- By using the above metrics and indicators, you can confidently read and analyze an income statement, making informed decisions about a company’s financial performance and stability.









